 2. Adding new rules
2. Adding new rules 
 2. Adding new rules
2. Adding new rules 
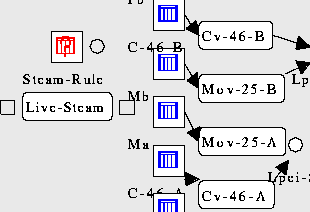
Figure 4. Model after creating "Steam-Rule" variable. Round boxes on the side of rule node are handles for connection to variables.
Because "Steam-Rule" is an unconditional rule it has no input handles, just a single output handle. We drag the output handle over the "Live-Steam" variable to connect them. Note also that the icon for the "Steam-Rule" has a question mark on it. This is because we haven't yet defined its valuation (in this case probability table). We do that next.
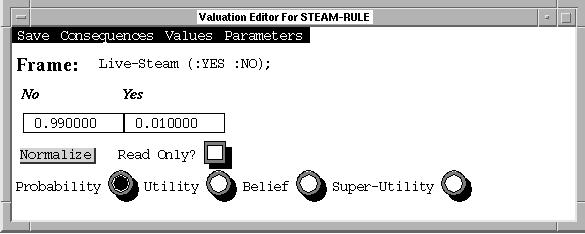
Figure 5. Valuation editor for "Steam-Rule".
Figure 5 shows the valuation editor for the steam rule. We fill in the probabilities in the appropriate boxes and save it. The icon on the "Steam-Rule" changes from the red undefined table to the blue defined table icon. We no longer need the rules "Ma" and "Mb" which defined the failure rates for the motor operated valves so we remove them by dragging them on top of the "green eater" in the corner of the screen. Next, we create the new class of rules to replace them.
 Continue with
this example and create a new class of
rules which describes the distribution of MOV failures conditioned on
the presence of live steam.
Continue with
this example and create a new class of
rules which describes the distribution of MOV failures conditioned on
the presence of live steam.
 Model Construction. Go back to the
begining of this example.
Model Construction. Go back to the
begining of this example.
 Return to
the main example page.
Return to
the main example page.
 Back to overview of Graphical-Belief.
Back to overview of Graphical-Belief.
 View a list
of Graphical-Belief in publications and downloadable technical
reports.
View a list
of Graphical-Belief in publications and downloadable technical
reports.
 The Graphical-Belief user
interface is implemented in Garnet.
The Graphical-Belief user
interface is implemented in Garnet.
 Get more
information about obtaining Graphical-Belief (and why
it is not generally available).
Get more
information about obtaining Graphical-Belief (and why
it is not generally available).
 get
the home page for Russell Almond , author
of Graphical-Belief.
get
the home page for Russell Almond , author
of Graphical-Belief.
 Click
here to get to the home page for Insightful (the company that StatSci
has eventually evolved into).
Click
here to get to the home page for Insightful (the company that StatSci
has eventually evolved into).